Oil Free Vacuum Pumps are becoming increasingly popular in a variety of industries due to their many advantages over traditional oil-lubricated pumps. These pumps offer a cleaner, more environmentally friendly solution for applications where oil contamination is a concern. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of oil free vacuum pumps, exploring their types, applications, advantages, and factors to consider when choosing the right one for your needs.
Understanding Oil Free Vacuum Pumps
Oil free vacuum pumps, as their name suggests, operate without the use of oil as a lubricant or sealant within the pump chamber. This eliminates the risk of oil contamination in the process or environment, making them ideal for sensitive applications. Instead of oil, these pumps utilize alternative mechanisms like dry lubrication, tight tolerances, or special pump designs to achieve vacuum.
Types of Oil Free Vacuum Pumps
There are several types of oil free vacuum pumps available, each with its own working principle and advantages:
1. Dry Screw Vacuum Pumps
Dry screw pumps utilize two spiral rotors that rotate within a housing. The precise fit and high rotational speed create a vacuum as gas is drawn in, compressed, and discharged. They are known for their efficiency, reliability, and ability to handle large gas volumes.
2. Diaphragm Vacuum Pumps
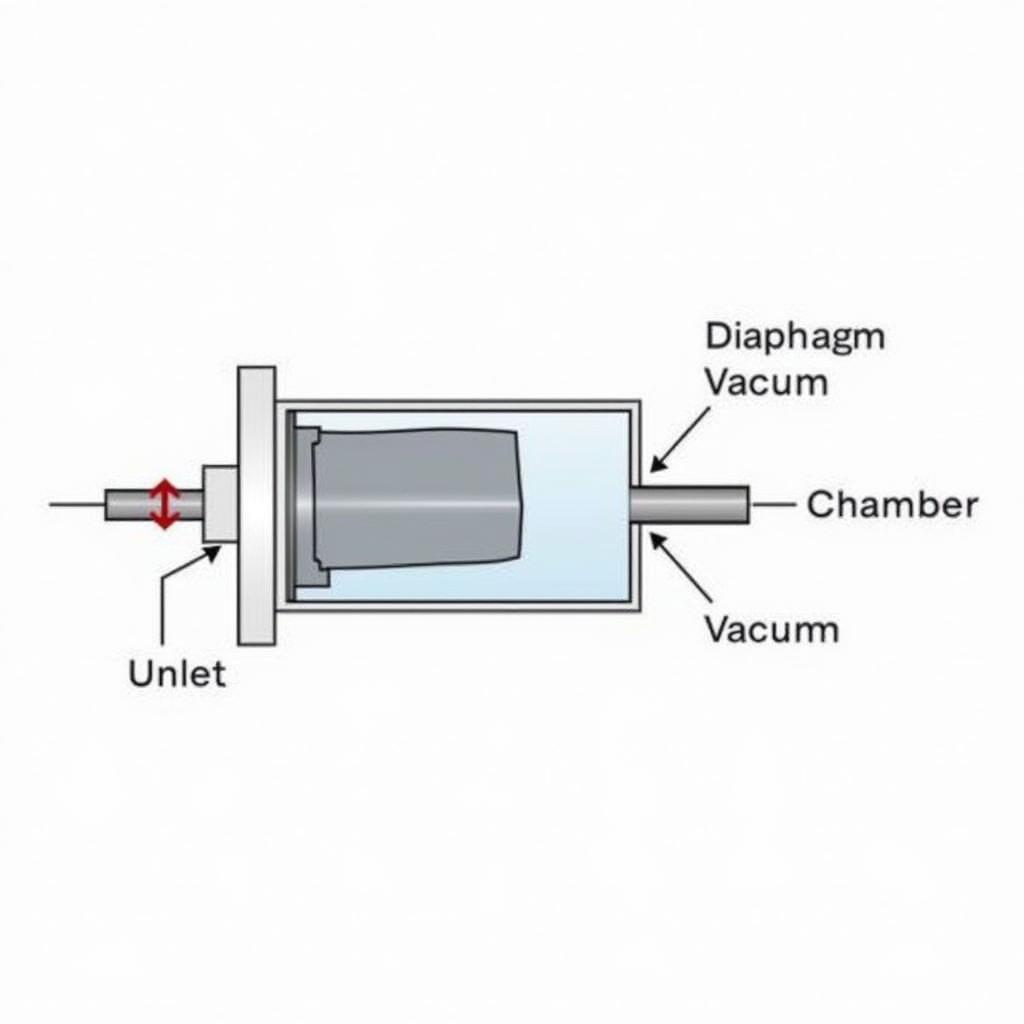 Diaphragm Vacuum Pump Diagram
Diaphragm Vacuum Pump Diagram
Diaphragm pumps employ a reciprocating diaphragm to create a vacuum. As the diaphragm flexes, it draws in gas, compresses it, and expels it through an outlet valve. These pumps are known for their dry operation, chemical resistance, and ability to handle both gases and vapors.
3. Scroll Vacuum Pumps
Scroll pumps consist of two spiral scrolls, one stationary and one orbiting eccentrically. This movement creates pockets that trap and compress gas, ultimately creating a vacuum. Scroll pumps are valued for their low vibration, quiet operation, and ability to achieve deep vacuum levels.
Advantages of Oil Free Vacuum Pumps
The growing popularity of oil free vacuum pumps can be attributed to their numerous benefits:
- Oil-free Operation: The most significant advantage is the elimination of oil contamination, making them suitable for applications requiring high purity levels.
- Environmental Friendliness: Without the need for oil disposal, these pumps offer a greener alternative, reducing environmental impact.
- Low Maintenance: Oil-free pumps generally require less maintenance compared to oil-lubricated pumps, as there’s no need for oil changes, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- High Efficiency: Many oil free pump designs operate with high efficiency, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs.
- Corrosion Resistance: The absence of oil often results in greater resistance to corrosion, extending the pump’s lifespan.
Applications of Oil Free Vacuum Pumps
Oil free vacuum pumps find applications in various industries, including:
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Used in medical devices, laboratory equipment, and pharmaceutical manufacturing where clean and sterile environments are critical.
- Food and Packaging: Employed in food processing, packaging, and bottling to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination.
- Electronics and Semiconductor: Used in semiconductor manufacturing, electronics assembly, and leak detection processes that demand a contaminant-free environment.
- Scientific Instruments: Utilized in mass spectrometers, electron microscopes, and other scientific instruments requiring precise vacuum levels and oil-free operation.
Choosing the Right Oil Free Vacuum Pump
Selecting the appropriate oil free vacuum pump for a specific application involves considering several factors:
- Required Vacuum Level: Different pumps are designed to achieve different vacuum levels, so understanding the required pressure is crucial.
- Pumping Speed: The pump’s capacity to remove a specific volume of gas per unit of time is another essential factor.
- Gas Compatibility: Ensure the pump’s materials are compatible with the gases being pumped to prevent corrosion or degradation.
- Operating Environment: Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and potential contaminants that could impact the pump’s performance.
- Maintenance Requirements: Evaluate the pump’s maintenance needs and choose a model that aligns with operational requirements.
Conclusion
Oil free vacuum pumps offer a reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for a wide range of applications where oil contamination is a concern. By understanding the different types, advantages, and selection criteria, you can choose the ideal oil free vacuum pump to meet your specific needs and optimize your operations.