Lead-free soldering wire has become the industry standard, replacing traditional tin-lead solder in most applications. This shift is driven by health and environmental concerns associated with lead exposure. Choosing the right lead-free solder wire is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient soldering results. This guide provides a detailed overview of lead-free soldering wire, its benefits, common types, and factors to consider when selecting the best option for your needs.
What is Lead-Free Soldering Wire?
Lead-free soldering wire, as its name suggests, is a type of solder that does not contain lead. It is typically composed of tin alloyed with other metals such as copper, silver, bismuth, and antimony. These alternative metals create a strong bond between electronic components without the harmful effects of lead.
 Lead-free solder wire spool
Lead-free solder wire spool
Why Go Lead-Free?
The primary reason for the transition to lead-free soldering is the toxicity of lead. Lead exposure poses significant health risks, especially to vulnerable populations like children and pregnant women. It can lead to developmental issues, neurological problems, and other serious health conditions. By using lead-free alternatives, manufacturers minimize the risk of lead contamination, safeguarding both human health and the environment.
Benefits of Lead-Free Soldering Wire
Beyond the crucial health and environmental benefits, lead-free soldering wire offers several advantages:
- Environmental Protection: Lead-free solder is environmentally friendly, reducing the release of lead into landfills and water sources.
- Improved Reliability: Lead-free alloys often have higher melting points, resulting in stronger and more durable solder joints that can withstand higher temperatures.
- Enhanced Performance: Some lead-free solders exhibit improved electrical conductivity and thermal performance compared to traditional lead-based solders.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many countries have implemented regulations restricting or banning the use of lead in electronics manufacturing. Using lead-free solder ensures compliance with these regulations.
Types of Lead-Free Soldering Wire
Various lead-free solder alloys are available, each with unique properties and applications:
1. Tin-Copper (SnCu)
Tin-copper alloys are among the most common lead-free options. They are known for their good wetting properties, making them suitable for a wide range of soldering tasks. SnCu solders typically have a higher melting point than tin-lead solder.
2. Tin-Silver (SnAg)
Tin-silver alloys offer excellent electrical conductivity and are often preferred for applications requiring high reliability, such as aerospace and medical devices. They also exhibit good thermal fatigue resistance.
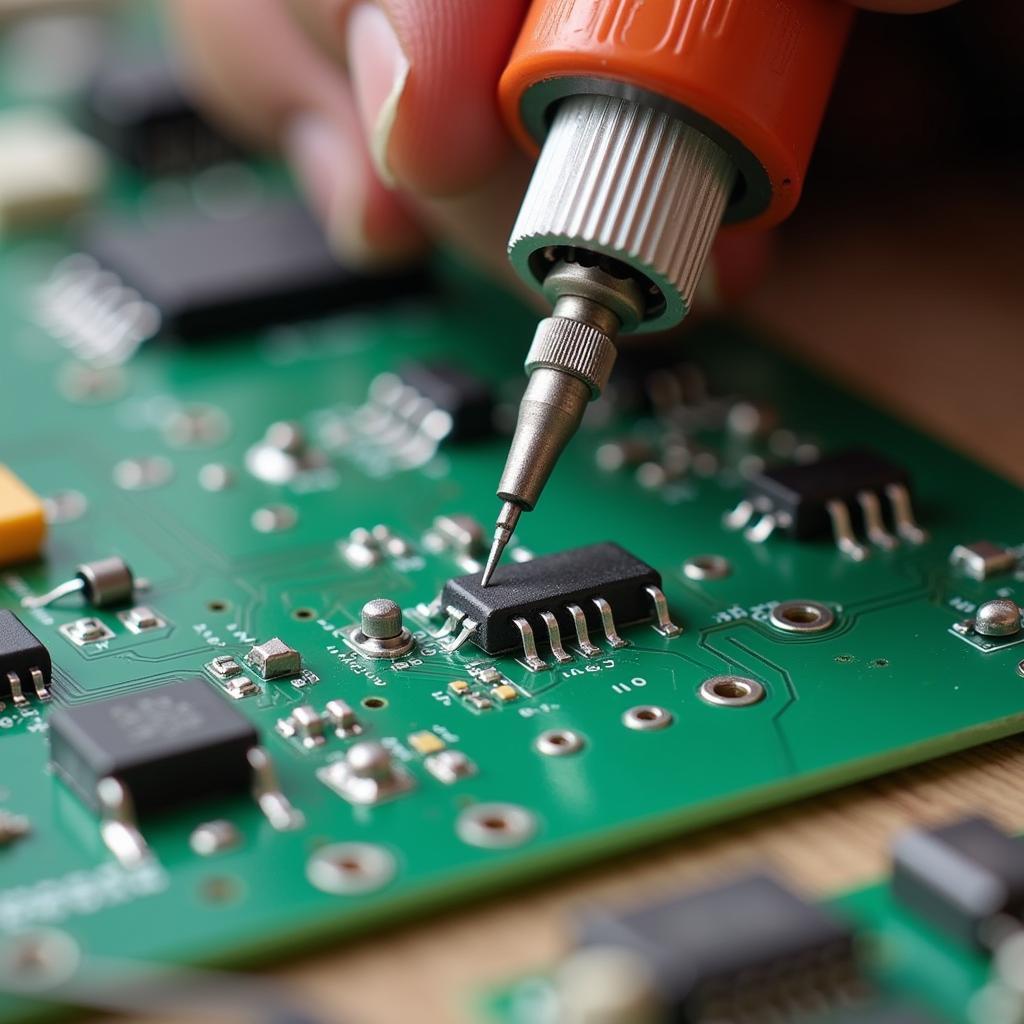 Soldering electronic components using lead-free solder wire
Soldering electronic components using lead-free solder wire
3. Tin-Silver-Copper (SAC)
SAC alloys combine the benefits of tin-copper and tin-silver, offering a balance of good wetting properties, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength. They are widely used in electronics manufacturing.
4. Tin-Bismuth (SnBi)
Tin-bismuth alloys have lower melting points compared to other lead-free options, making them suitable for delicate components sensitive to high temperatures. However, their use in high-reliability applications is limited due to lower mechanical strength.
Choosing the Right Lead-Free Soldering Wire
Selecting the appropriate lead-free soldering wire depends on several factors:
- Application: The specific application dictates the required solder properties, such as melting point, strength, and conductivity.
- Component Sensitivity: Consider the heat sensitivity of the components being soldered.
- Soldering Iron Temperature: Choose a solder with a melting point compatible with your soldering iron’s temperature range.
- Flux Core: The flux core within the solder wire removes oxides and promotes good wetting. Select a flux core appropriate for the metals being soldered.
- Diameter: Solder wire diameter should match the size of the components and soldering iron tip.
Conclusion
Lead-free soldering wire is essential for responsible electronics manufacturing, protecting human health and the environment. By understanding the different types of lead-free solders and considering the factors discussed above, you can select the right wire for your soldering needs, ensuring reliable and high-quality results.